CPU Chip
1. CPU Chip
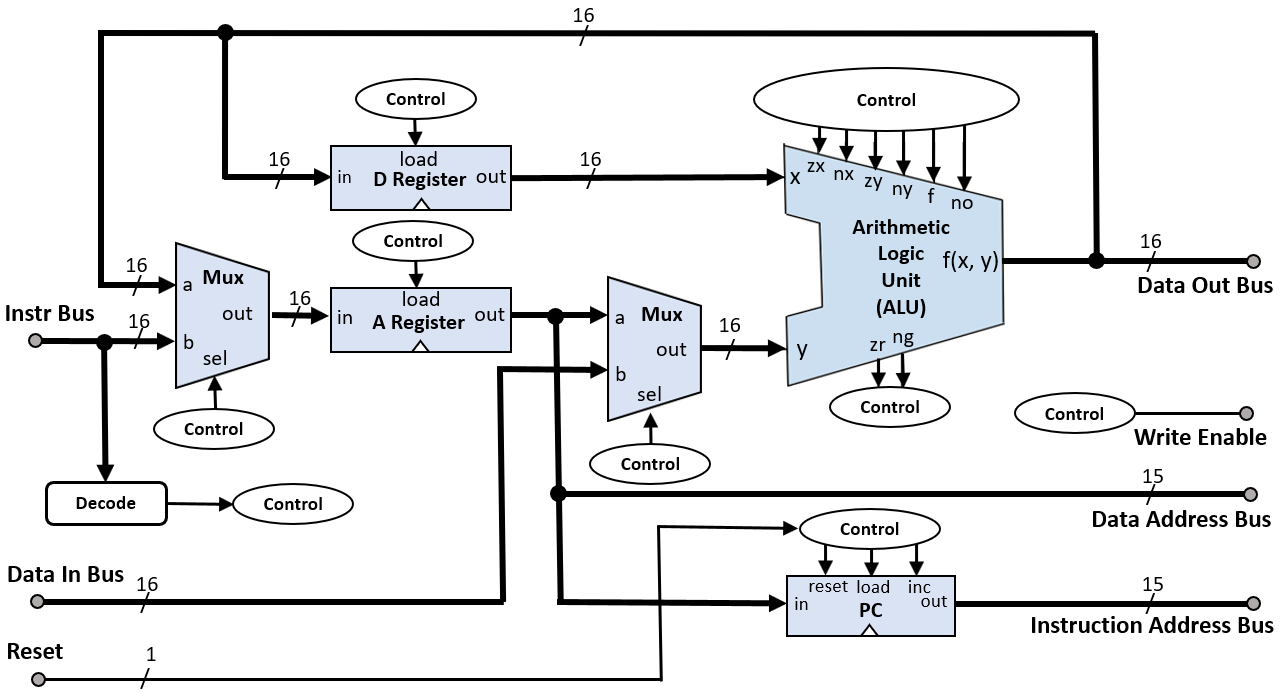
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of the Hack computer. It:
Executes instructions received from memory.
Handles both A-instructions (addressing) and C-instructions (computation).
Controls the Program Counter (PC).
Interfaces with Memory, ALU, and A/D registers.
It receives a 16-bit instruction and computes the next values for the outM, writeM, addressM, and pc outputs.
2. Truth Table
| instruction[15] | Type | Operation |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | A-instruction | Set A register to instruction[0..14] |
| 1 | C-instruction | Perform ALU operation and control flow |
Key outputs and behaviors:
| input | output | Description |
|---|---|---|
| instruction | outM | ALU result, to be written to memory (if writeM = 1) |
| instruction[3] | writeM | Set to 1 if result is to be written to memory |
| instruction[0..2] | jump bits | Determine whether to jump based on ALU output |
| ALU out == 0 | Jump if j1 or j2 is set | Conditional jump logic |
| instruction[10..6] | comp bits | Determines ALU computation |
| instruction[5..3] | dest bits | Where to store ALU result (A, D, or M) |
| reset == 1 | pc = 0 | Forces PC to reset |
3. Implementation (HDL)
The CPU combines the ALU, Register, and Program Counter (PC), and routes control based on instruction bits.
CHIP CPU {
IN inM[16], instruction[16], reset;
OUT outM[16], writeM, addressM[15], pc[15];
PARTS:
// Instruction Decoding
Not(in=instruction[15], out=isAInstruction);
// A-instruction handling
Mux16(a=aluOut, b=instruction[0..15], sel=isAInstruction, out=aIn);
// A register (can be loaded by both A- and C-instructions)
Or(a=isAInstruction, b=instruction[5], out=loadA);
Register(in=aIn, load=loadA, out=aOut);
// D register
Register(in=aluOut, load=instruction[4], out=dOut);
// Select input for ALU
Mux16(a=aOut, b=inM, sel=instruction[12], out=aluY);
// ALU
ALU(x=dOut, y=aluY,
zx=instruction[11], nx=instruction[10],
zy=instruction[9], ny=instruction[8],
f=instruction[7], no=instruction[6],
out=aluOut, zr=zr, ng=ng);
// Destination and write
And(a=instruction[3], b=instruction[15], out=writeM);
And(a=instruction[5], b=instruction[15], out=loadAFromALU);
And(a=instruction[4], b=instruction[15], out=loadD);
// Address to memory (from A register)
Assign(addressM = aOut);
// Output from CPU to memory
Assign(outM = aluOut);
// Program Counter logic
// Determine jump conditions
Not(in=zr, out=notZr);
Not(in=ng, out=notNg);
And(a=notZr, b=notNg, out=pos);
And(a=notZr, b=ng, out=neg);
And(a=zr, b=notNg, out=zero);
And(a=instruction[0], b=pos, out=jgt);
And(a=instruction[1], b=zero, out=jeq);
And(a=instruction[2], b=neg, out=jlt);
Or(a=jlt, b=jeq, out=jlteq);
Or(a=jlteq, b=jgt, out=jump);
And(a=instruction[15], b=jump, out=pcLoad);
// PC
PC(in=aOut, load=pcLoad, inc=true, reset=reset, out=pc);
}