Hack Assembler
1. Description
The Hack Assembler is a software tool that translates Hack assembly code (.asm) into binary machine code (.hack) that can be executed by the Hack computer platform.
This project marks the final step in Nand2Tetris Part I, combining everything learned about binary computation, instruction formats, and symbolic parsing.
This assembler performs:
Two-pass translation
Symbol resolution (labels and variables)
Instruction decoding (A and C types)
2. High-Level Architecture
Input: Assembly (.asm)
↓
[Pass 1] → Resolve Labels → Update symbol table
↓
[Pass 2] → Translate Instructions → Output binary
↓
Output: Binary (.hack)
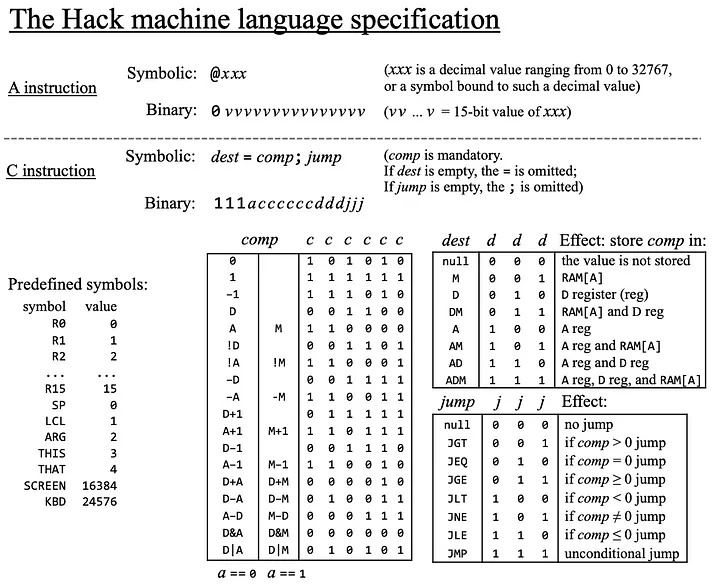
3. Key Concepts
A-Instructions (@value)
Represent memory addresses
@21 becomes 0000000000010101
@LOOP resolves to the address of a label
C-Instructions (dest=comp;jump)
Represent computations and control flow
D=A+1 → computation from comp_table, dest_table
D;JGT → uses jump_table
Labels and Symbols
(LOOP) labels are resolved in the first pass
New variables like @i start from address 16
4. Tables Used
comp_table (Selected Examples)
| comp | Binary |
|---|---|
| D+1 | 0011111 |
| A-1 | 0110010 |
| D|M | 1010101 |
| comp | Binary |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0101010 |
| 1 | 0111111 |
| -1 | 0111010 |
| D | 0001100 |
| A | 0110000 |
| M | 1110000 |
| !D | 0001101 |
| !A | 0110001 |
| !M | 1110001 |
| -D | 0001111 |
| -A | 0110011 |
| -M | 1110011 |
| D+1 | 0011111 |
| A+1 | 0110111 |
| M+1 | 1110111 |
| D-1 | 0001110 |
| A-1 | 0110010 |
| M-1 | 1110010 |
| D+A | 0000010 |
| D+M | 1000010 |
| D-A | 0010011 |
| D-M | 1010011 |
| A-D | 0000111 |
| M-D | 1000111 |
| D&A | 0000000 |
| D&M | 1000000 |
| D|A | 0010101 |
| D|M | 1010101 |
dest_table
| dest | Binary |
|---|---|
| 000 | |
| M | 001 |
| D | 010 |
| MD | 011 |
| A | 100 |
| AM | 101 |
| AD | 110 |
| AMD | 111 |
jump_table
| jump | Binary |
|---|---|
| 000 | |
| JGT | 001 |
| JEQ | 010 |
| JGE | 011 |
| JLT | 100 |
| JNE | 101 |
| JLE | 110 |
| JMP | 111 |
5. Symbol Table (Built-In)
| Symbol | Address |
|---|---|
| SP | 0 |
| LCL | 1 |
| ARG | 2 |
| THIS | 3 |
| THAT | 4 |
| R0–R15 | 0–15 |
| SCREEN | 16384 |
| KBD | 24576 |
| Variables | 16+ |
6. Code Structure (Python)
Main Phases:
first_pass(lines)
Resolves labels like (LOOP) into ROM addresses.
second_pass(lines)
Translates each instruction into a 16-bit binary string. Handles:
A-instructions: direct or symbolic
C-instructions: parsed into dest=comp;jump
assemble(file.asm)
Calls both passes and writes output to .hack
CLI Usage:
python assembler.py Mult.asm
7. Example Translation
Assembly Input
@R0
D=M
@R1
D=D+M
@R2
M=D
Binary Input
0000000000000000
1111110000010000
0000000000000001
1111000010010000
0000000000000010
1110001100001000
8. Project Files
| File Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
assembler.py | Main assembler script |
Add.asm | Example input program |
Add.hack | Output from running assembler |
SymbolTable.md | Reference table (optional) |
9. Test Strategy
Run .asm files from the projects/06 folder (like Max.asm, Rect.asm, Mult.asm)
Load .hack output into CPU Emulator
Compare against .cmp files or visually verify behavior
10. Code (Python)
import sys
import re
# Predefined symbols
symbol_table = {
"SP": 0, "LCL": 1, "ARG": 2, "THIS": 3, "THAT": 4,
"SCREEN": 16384, "KBD": 24576,
**{f"R{i}": i for i in range(16)}
}
# Binary lookup tables
comp_table = {
# a = 0
"0": "0101010", "1": "0111111", "-1": "0111010",
"D": "0001100", "A": "0110000", "!D": "0001101",
"!A": "0110001", "-D": "0001111", "-A": "0110011",
"D+1": "0011111", "A+1": "0110111", "D-1": "0001110",
"A-1": "0110010", "D+A": "0000010", "D-A": "0010011",
"A-D": "0000111", "D&A": "0000000", "D|A": "0010101",
# a = 1
"M": "1110000", "!M": "1110001", "-M": "1110011",
"M+1": "1110111", "M-1": "1110010", "D+M": "1000010",
"D-M": "1010011", "M-D": "1000111", "D&M": "1000000",
"D|M": "1010101"
}
dest_table = {
"": "000", "M": "001", "D": "010", "MD": "011",
"A": "100", "AM": "101", "AD": "110", "AMD": "111"
}
jump_table = {
"": "000", "JGT": "001", "JEQ": "010", "JGE": "011",
"JLT": "100", "JNE": "101", "JLE": "110", "JMP": "111"
}
# Clean a line of comments and whitespace
def clean(line):
return re.sub("//.*", "", line).strip()
# First pass: resolve labels
def first_pass(lines):
rom = 0
for line in lines:
line = clean(line)
if not line:
continue
if line.startswith("("):
label = line[1:-1]
symbol_table[label] = rom
else:
rom += 1
# Second pass: generate binary code
def second_pass(lines):
ram_address = 16
binary_lines = []
for line in lines:
line = clean(line)
if not line or line.startswith("("):
continue
if line.startswith("@"): # A-instruction
symbol = line[1:]
if symbol.isdigit():
address = int(symbol)
else:
if symbol not in symbol_table:
symbol_table[symbol] = ram_address
ram_address += 1
address = symbol_table[symbol]
binary_lines.append(f"{address:016b}")
else: # C-instruction
if "=" in line:
dest, comp_jump = line.split("=")
else:
dest, comp_jump = "", line
if ";" in comp_jump:
comp, jump = comp_jump.split(";")
else:
comp, jump = comp_jump, ""
comp_bits = comp_table.get(comp.strip(), "0000000")
dest_bits = dest_table.get(dest.strip(), "000")
jump_bits = jump_table.get(jump.strip(), "000")
binary_lines.append("111" + comp_bits + dest_bits + jump_bits)
return binary_lines
# Main assembler function
def assemble(asm_path, hack_path=None):
with open(asm_path, 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
first_pass(lines)
binary = second_pass(lines)
out_path = hack_path or asm_path.replace(".asm", ".hack")
with open(out_path, 'w') as file:
file.write("\n".join(binary))
print(f"Assembly complete: {out_path}")
# If running from CLI
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python assembler.py <file.asm>")
else:
assemble(sys.argv[1])